Are your gums frequently red or swollen? This could be a sign of gingivitis, a common but mild gum disease. In this blog post, we’ll guide you through the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for gingivitis to help you take charge of your oral health.
Don’t let gingivitis steal your smile!
Gingivitis Overview
Are you noticing red, swollen gums whenever you brush or floss? You might be dealing with a common gum problem called gingivitis. Our complete guide will help you understand the causes and symptoms of this condition, along with effective treatment options.
Let’s dive into what it takes to keep your smile healthy.
Causes of Gingivitis
Periodontal bacteria and various risk factors contribute to the development of gingivitis.
Periodontal Bacteria
Bacteria in your mouth can lead to gingivitis. This kind of bacteria is called periodontal bacteria. When you eat food, some bits stick on your teeth. The bacteria feed on this food and form a film called plaque.
If not cleaned off, the plaque hardens into tartar. Tartar hurts gums and makes them red, puffy, and bleed easily.
Plaque overgrowth leads to more periodontal bacteria in your mouth. These harmful types cause gum tissue destruction and other bad effects like bleeding gums or tender gums. They are one main cause of gingivitis that’s why it’s important for everyone to maintain good oral hygiene by brushing teeth daily and having regular dental checkups.
Other Risk Factors
Gingivitis can stem from many risks. Some of these include:
- Smoking: Cigarettes and other tobacco products can harm gums and increase the risk of gum disease.
- Older Age: As we age, our gums may get weaker. This makes them more likely to have gingivitis.
- Dry Mouth: Low saliva production makes it easier for bacteria to grow in the mouth, leading to gingivitis.
- Poor Nutrition: Not eating right puts our teeth and gums at risk too. A lack of vitamin C or B12 is bad for oral health.
- Medical Conditions: Illnesses like diabetes or HIV/AIDS can make someone more likely to get gingivitis.
- Certain Medications: Drugs that limit saliva flow like Phenyoitin and calcium channel blockers can cause oral health issues.
- Hormonal Changes: Times of hormone swings such as pregnancy or menstrual cycle can lead to swollen and tender gums.
Symptoms of Gingivitis
Gingivitis presents symptoms such as red and swollen gums, bleeding gums, and bad breath.
Red and Swollen Gums
Red and swollen gums are a sign of gingivitis. Gingivitis is when your gums get sore. They turn dusky red and puff up. This happens because of plaque build-up on your teeth from not brushing or flossing well.
Your gums might feel tender and bleed easily, especially when you brush or floss. It’s very important to care for your teeth to avoid getting gingivitis. If it gets worse, it can lead to serious gum disease called periodontitis and even cause tooth loss.
Bleeding Gums
Bleeding gums are one of the symptoms of gingivitis, which is a mild form of gum disease. When you have bleeding gums, it means that your gum tissue is irritated and inflamed. This can happen when plaque builds up on your teeth and along the gumline.
Plaque is a sticky film that contains bacteria. If you don’t brush and floss regularly, the bacteria in plaque can cause your gums to become red, swollen, and tender. When you brush or floss your teeth, you may notice that your gums bleed easily.
It’s important not to ignore this symptom as it could be a sign of gingivitis or even more severe gum disease if left untreated.
Poor oral hygiene is often the main cause of bleeding gums. By not properly cleaning your teeth and removing plaque regularly through brushing and flossing, you increase your risk for developing gingivitis.
Other factors that can contribute to bleeding gums include smoking, older age, dry mouth (which reduces saliva production), poor nutrition (especially low vitamin C levels), and certain medical conditions like diabetes or leukemia.
If you notice that your gums bleed when brushing or flossing, it’s essential to see a dental professional for evaluation and treatment. They can determine if gingivitis is present by performing a thorough examination of your mouth and possibly taking X-rays.
Treating bleeding gums promptly can help prevent further complications like periodontitis (a more advanced form of gum disease) which could result in tooth loss if left untreated.
Bad Breath
Bad breath, also known as halitosis, is one of the common symptoms of gingivitis. It occurs when bacteria in the mouth produce strong-smelling compounds. Poor oral hygiene leads to the build-up of plaque on teeth, which can cause bad breath.
In addition to this, certain systemic diseases such as respiratory disease, diabetes, coronary artery disease, stroke, and rheumatoid arthritis can contribute to bad breath. When left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis and lead to tooth loss.
So it’s important to maintain good oral hygiene practices and visit a dentist regularly for check-ups.
Diagnosis of Gingivitis
Diagnosing gingivitis involves a dental examination and X-rays to determine the extent of gum disease. Find out more about the diagnosis process in our blog post.
Dental Examination
During a dental examination, the dentist will visually examine your gums and may also take X-rays to check for signs of gingivitis. They may use a probe to measure the depth of spaces between your teeth and gums, which can help determine if there is gum inflammation or bleeding.
The dentist will also review your medical and dental history to gather important information that can contribute to the diagnosis of gingivitis. This thorough examination is essential in identifying any potential issues with your gums and starting appropriate treatment.
X-Rays
X-Rays are important in diagnosing gingivitis. They can help healthcare professionals understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition. X-Rays may be ordered to check for bone loss, which is a common complication of gingivitis.
By examining the X-Ray images, dentists can see if there is any damage or deterioration in the bone that supports the teeth. This information helps them develop an appropriate treatment plan for their patients.
So, X-Rays play a crucial role in detecting and managing gingivitis effectively.
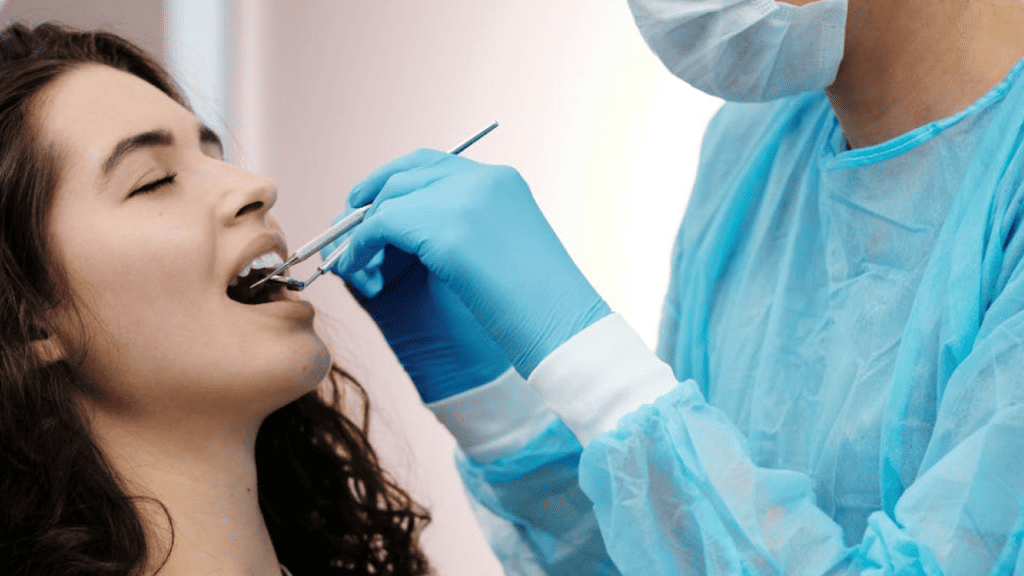
Treatment Options for Gingivitis
Treatment options for gingivitis include professional dental cleaning, medications, and surgery. Discover the most effective ways to combat this common oral health issue in our comprehensive guide.
Professional Dental Cleaning
Professional dental cleaning is a crucial treatment for gingivitis. During the cleaning, a dental professional will carefully remove plaque and tartar from your teeth and along the gumline.
This helps to reduce inflammation and prevent further damage to your gums. The dentist or hygienist will also polish your teeth to remove surface stains and make them smooth. Regular professional cleanings can effectively treat gingivitis and maintain good oral health.
Remember, treating gingivitis promptly can reverse damage and prevent it from progressing to more severe gum disease. Prevention of gingivitis involves practicing regular oral hygiene, such as brushing twice a day, flossing daily, using mouthwash, and scheduling regular dental check-ups.
Medications
Medications can cause or worsen gingivitis. Some medications that can contribute to gingivitis include phenytoin, cyclosporine, calcium channel blockers, and oral or injectable birth control. These medications may increase the risk of gum disease and impact oral health. It’s important to be aware of these potential side effects when taking these medications. Additionally, certain antibiotics like doxycycline can be used to treat gingivitis. Timed-release antiseptic chips and oral antibiotics may also be prescribed by a dental professional to help treat gum disease.
Surgery
Surgery is an option for people with severe cases of gingivitis. When other treatments don’t work or the condition has gotten worse, surgery may be recommended by dental professionals.
The goal of surgery is to remove the infected gum tissue and promote healing. This can involve procedures like gum flap surgery or a gingivectomy, where the diseased gum tissue is cut away.
Surgery can help reduce inflammation and prevent further damage to the gums and teeth. It’s important to follow post-surgery instructions from your dentist to ensure proper healing and maintain good oral hygiene habits afterwards.
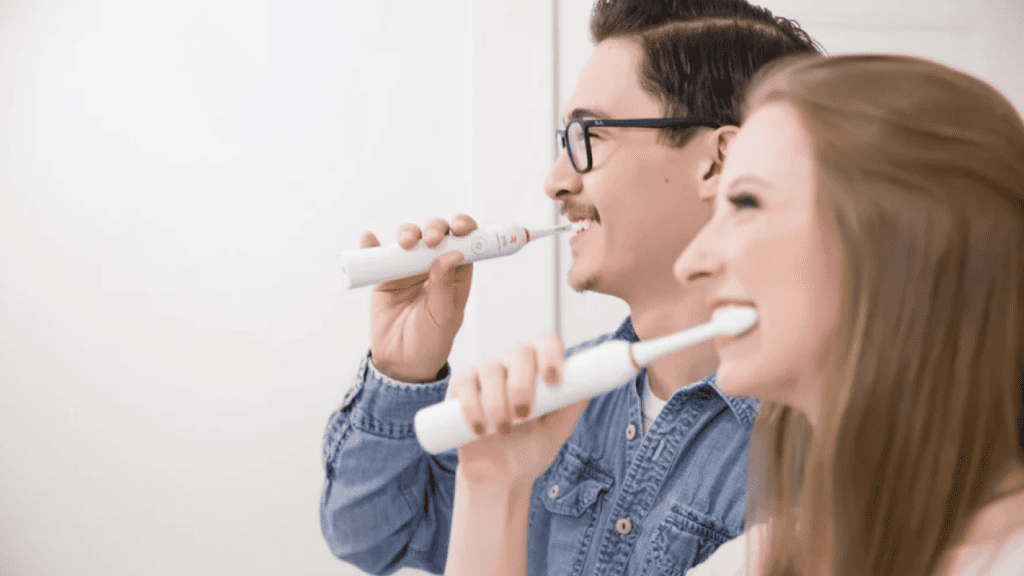

Prevention of Gingivitis
Maintain regular oral hygiene and schedule routine dental checkups to prevent gingivitis.
Regular Oral Hygiene
Keeping your mouth clean is important in preventing and treating gingivitis. Here are some ways to maintain regular oral hygiene:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day, using an electric toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste.
- Make sure to brush all surfaces of your teeth, including the gumline.
- Use dental floss or interdental brushes to clean between your teeth and remove plaque.
- Rinse your mouth with an antiseptic mouthwash to kill bacteria and freshen breath.
- Visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and checkups.
- Follow any instructions given by your dental health professional to ensure proper oral care.
Regular Dental Checkups
Regular dental checkups are crucial for maintaining good oral health and preventing gum diseases like gingivitis. These checkups, along with practicing proper oral hygiene at home, can help prevent and even reverse the early stages of gingivitis.
By visiting your dentist regularly, any potential issues can be identified and addressed before they become more serious. Additionally, during these visits, you will receive professional cleanings that remove plaque buildup and help prevent the development of gingivitis.
Remember to schedule regular dental checkups to keep your gums healthy and maintain a beautiful smile.
Complications of Untreated Gingivitis
If gingivitis is left untreated, it can lead to more serious complications. One of the main risks is that it can progress into a condition called periodontitis, which affects not only the gums but also the bones and tissues supporting the teeth.
This can eventually result in tooth loss.
Untreated gingivitis has also been linked to systemic diseases such as respiratory disease, diabetes, coronary artery disease, stroke, and rheumatoid arthritis. The inflammation caused by gum disease may contribute to these conditions or worsen existing ones.
In severe cases of gingivitis, a condition known as trench mouth or necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (NUG) can develop. It causes painful gums and ulcerations that can make eating and talking difficult.
Other complications of untreated gingivitis include recurrent episodes of gingivitis, infection or abscesses in the gums or jawbones, swollen lymph nodes in the neck area, and an increased risk of premature birth and low birth weight in pregnant women.
It’s important to take care of your oral health by practicing regular oral hygiene habits like brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily. Additionally, scheduling regular dental checkups will ensure early detection and treatment of any gum problems before they become more serious complications.
Conclusion
To sum it up, gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums that can lead to tooth loss if not treated. Poor oral hygiene is the main culprit, but smoking and certain medical conditions can also increase the risk.
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for reversing damage and preventing more serious gum disease. By practicing good oral hygiene habits and visiting your dentist regularly, you can keep your gums healthy and prevent gingivitis from causing further complications.
Stay proactive about caring for your oral health to ensure a bright smile for years to come!
Related Articles
Orange Plaque On Teeth: Causes and Treatment
Extreme Tooth Pain Can’t Sleep: What you need to know
Gum Abscess Popped By Itself (What To Do)
Marcus Ramsey has been a professional writer for over seven years. He has talked about and produced content for industries like Dentistry, Healthcare, and more.